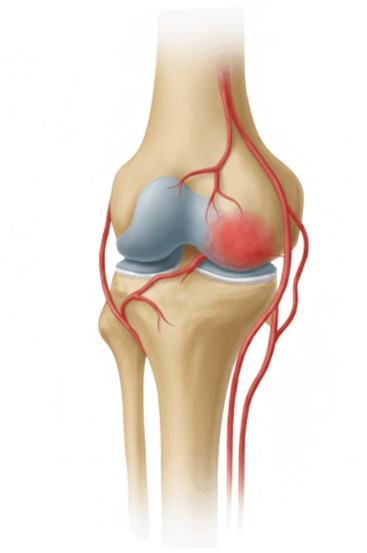
Genicular Artery Embolization (GAE)
- Relief for Chronic Knee Pain Without Surgery
- Living with persistent knee pain can be frustrating, especially when medications, injections, or physical therapy no longer help.
- Genicular Artery Embolization (GAE) is a minimally invasive, image-guided treatment that targets the source of inflammation in the knee to reduce pain and improve function—without surgery or a knee replacement.

Globally recognized innovator, Dr. Ram K Gurajala MD, leads the frontier with patented technologies, 40+ pioneering publications, and breakthroughs that redefine vascular care for patients in Hyderabad, Chennai, and across India.





Redefining Joint Pain Treatment - Minimally Invasive - Targets Inflammation at the Source - Cuts Off Blood Supply to Pain
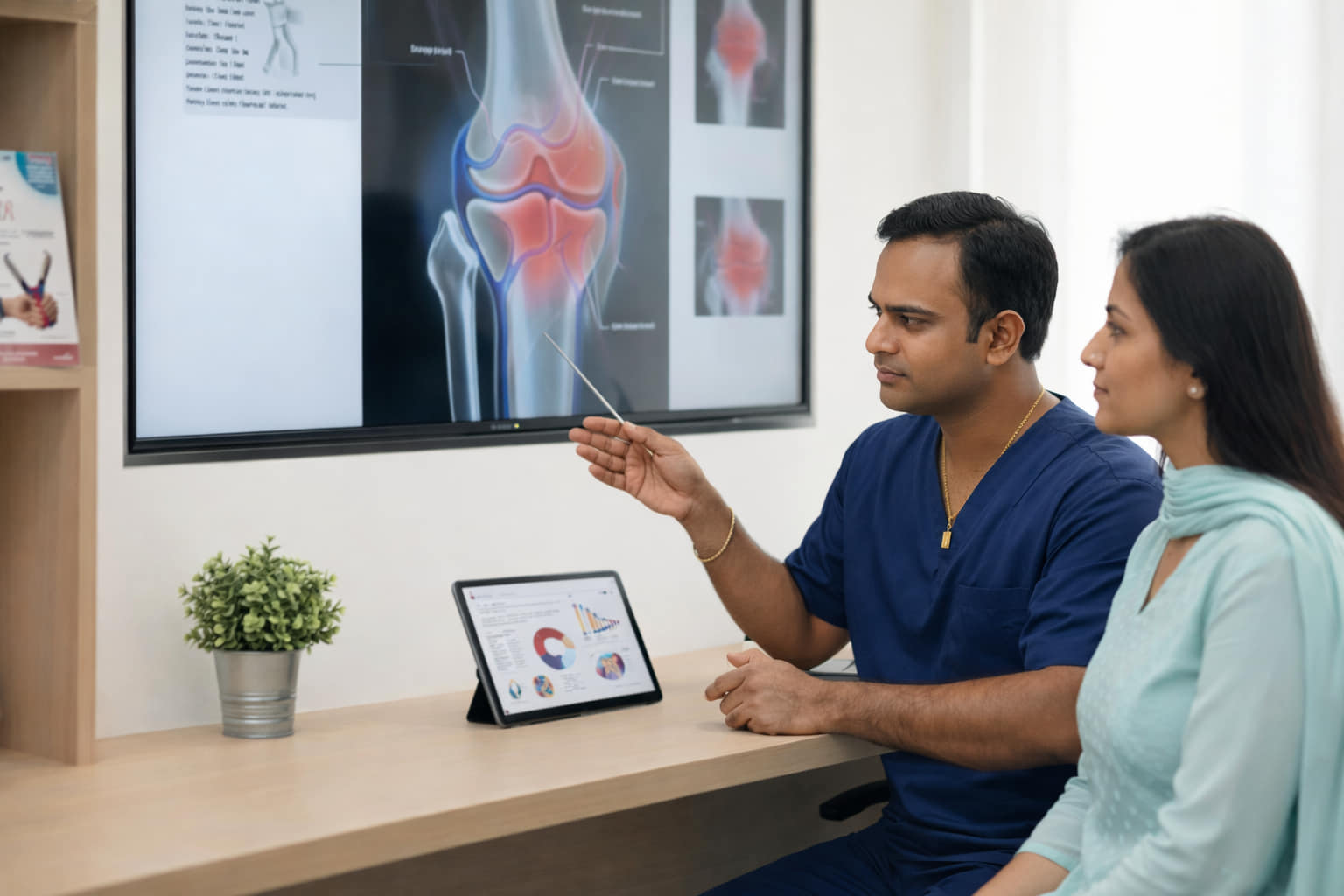
What Is Genicular Artery Embolization (GAE)?
GAE is a novel, image-guided treatment developed to relieve chronic knee pain by blocking abnormal blood vessels in the joint. The procedure involves injecting tiny embolic agents—such as particles or coils—into specific genicular arteries, thereby reducing excess blood flow that fuels inflammation and pain.
🔬 How GAE Works: Targeting the Source of Pain
In osteoarthritic joints, abnormal neovascularization—the formation of new, fragile blood vessels—plays a key role in inflammation and pain. GAE targets these vessels with precision:
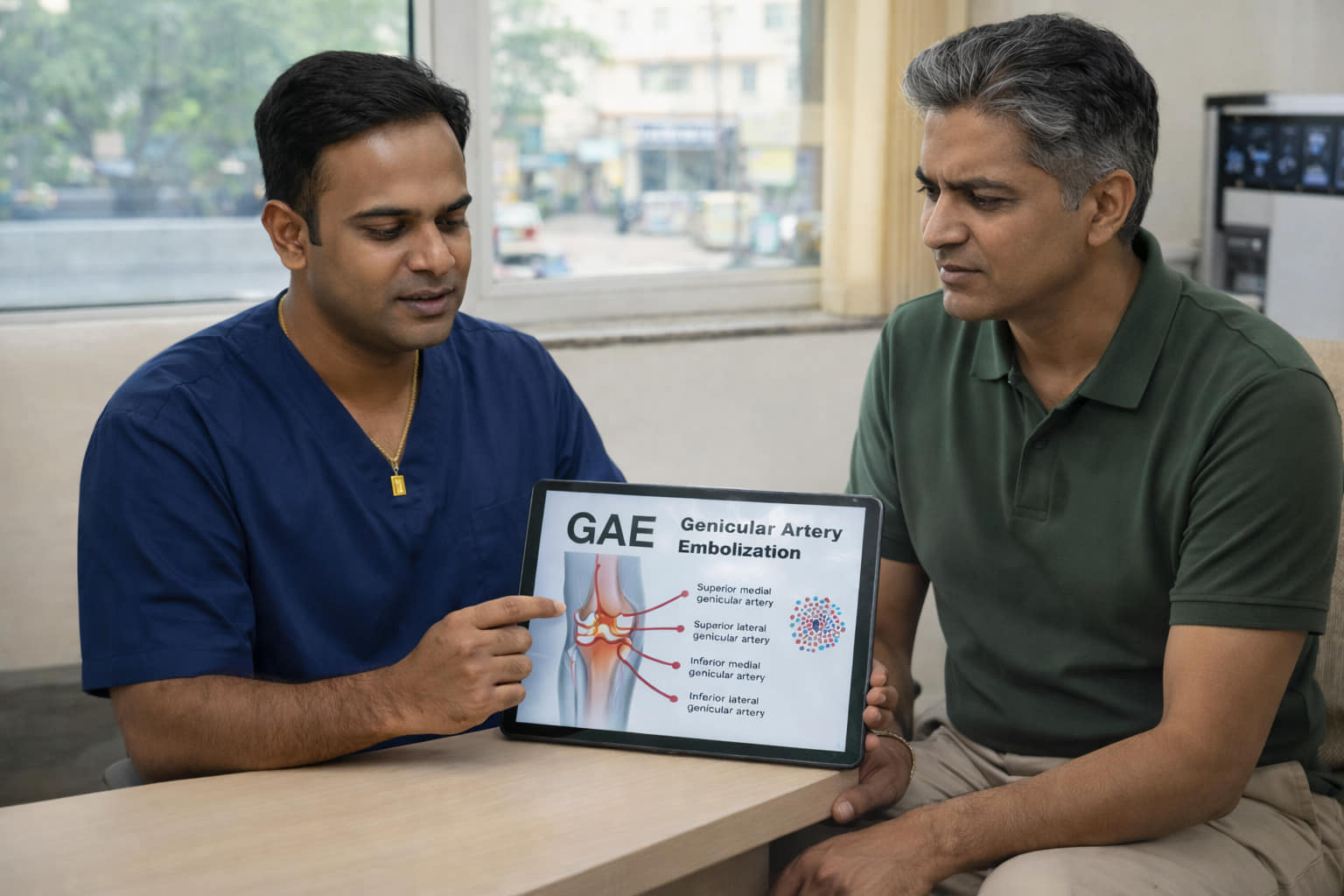
- Step 1: Under angiographic guidance, the interventional radiologist maps the network of genicular arteries that supply the inflamed joint.
- Step 2: Embolic materials are introduced to selectively block these vessels.
- Step 3: Blood flow to the painful areas is reduced, leading to less inflammation and pain.
Who Is a Candidate for GAE?
GAE is not for everyone—but it’s proving especially valuable in the following scenarios:
- Patients with chronic knee OA pain who haven’t responded to physical therapy, medications, or injections.
- Individuals with recurrent bleeding in the knee after TKA.
- Those who are not eligible for surgery due to medical comorbidities or prefer to avoid/delay knee replacement.
Important: A thorough clinical and radiologic evaluation is required to determine if GAE is appropriate. It’s a case-by-case decision made by an experienced interventional radiologist.
🧪 The Procedure: What to Expect
GAE is performed in an angiography suite and typically involves the following:
- Moderate sedation (no general anesthesia).
- Access through a small incision in the groin or wrist to reach the genicular arteries.
- Use of real-time imaging (angiography) to identify and target abnormal vessels.
- Injection of microspheres or particles into the genicular arteries.
- Duration: Usually completed within a few hours.
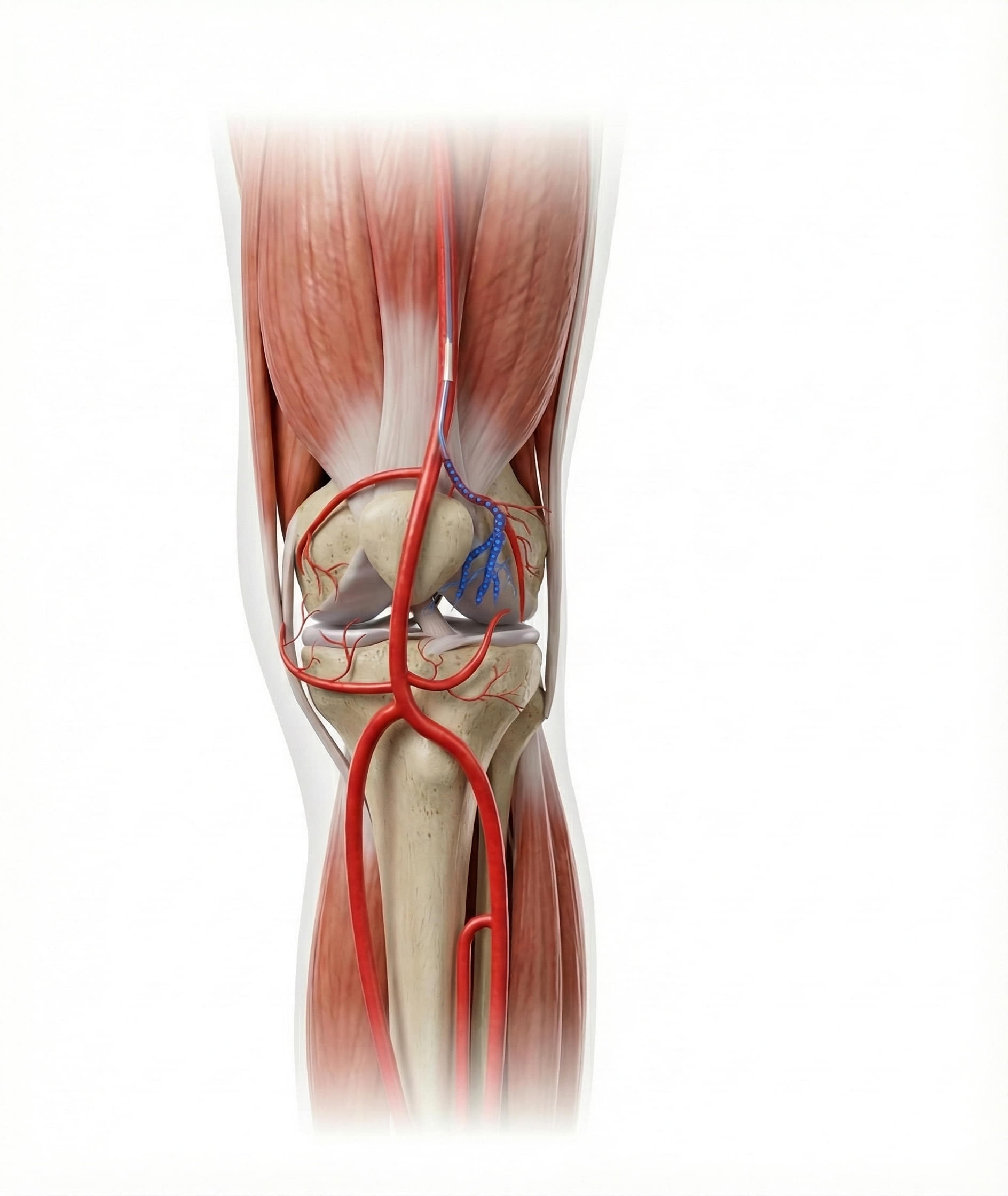
Why Anatomy Matters
Success depends heavily on the operator’s detailed knowledge of genicular artery anatomy, including its variations. Accurate targeting helps maximize efficacy and minimize risks like non-target embolization.
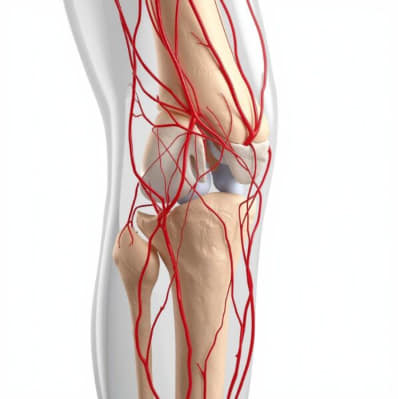
✅ Effectiveness and Recovery
Proven Benefits:
Clinical studies and case reports show:
- Reduced pain and stiffness
- Improved joint mobility and function
- Enhanced quality of life
Effective resolution of hemarthrosis post-knee surgery
Recovery Timeline:
- Most patients resume daily activities within a few days
- Some may experience mild discomfort or bruising at the puncture site
- Repeat procedures may be considered if symptoms recur over time

Redefining Joint Pain Treatment - Minimally Invasive - Targets Inflammation at the Source - Cuts Off Blood Supply to Pain

I was terrified of getting a knee replacement. The idea of a long recovery and major surgery was just too much for me. When I heard about GAE—a pinhole procedure with no stitches—I was skeptical but hopeful. I’m so glad I did it. The procedure was quick, I went home the same day, and within two weeks, the swelling and pain had dropped significantly. I can finally walk down the stairs without holding the railing for dear life!
— Kalsan R
Hyderabad

It emphasizes that this is for when "others say it's impossible."
Genicular Artery Embolization isn't just novel—it’s a game-changer for debilitating knee pain.
If you or someone you know is suffering from persistent knee pain and exploring alternatives to surgery, talk to an interventional radiologist about whether GAE could be the solution.
-
Advanced treatments
-
Personalized approach
-
Compassionate comfort
Common questions
Frequently asked questions about Genicular Artery Embolization
❓ What exactly is Genicular Artery Embolization (GAE)?
GAE is a minimally invasive, non-surgical procedure designed to reduce knee pain caused by osteoarthritis. It works by reducing the blood flow to the inflamed lining of the knee (the synovium), which is often the source of chronic pain.
❓ Is it painful?
The procedure itself is not painful. You are given local anesthesia and "twilight" sedation to keep you relaxed. Some patients experience temporary knee pain or skin discoloration for 1–3 days after the procedure as the inflammation subsides.
❓ How long does it take?
The procedure usually takes about 1 to 2 hours. You will spend a short time in recovery and can go home the same day.
❓ Does having GAE prevent me from getting a knee replacement later?
No. GAE does not burn any bridges. If your arthritis progresses significantly in the future, you can still have total knee replacement surgery. GAE is often used to delay the need for that surgery for years.
❓ Are there any side effects?
GAE is very safe. Minor side effects can include transient skin discoloration over the knee or temporary soreness. Serious complications are extremely rare.
❓ How is this different from Genicular Nerve Ablation (GNA)?
This is a common question. Nerve Ablation burns the nerve endings to stop pain signals from reaching the brain. GAE blocks the blood flow to stop the inflammation that causes the pain in the first place. Dr. Ram can help you decide which is better for your specific type of knee pain.
❓ What exactly are the "particles" you inject? Are they safe?
The particles are tiny, microscopic spheres made of a medical-grade, biocompatible material. They are widely used in many other medical procedures (like treating uterine fibroids or stopping bleeding). They are designed to remain permanently in the tiny vessels to keep them blocked, but you will not feel them.
